前言
[]在数组中比较常用,因为是取下标查看用的。
正文
但是[]重载只能作为类的方法
返回类型 operator[](类型 操作数);
拿我们自己写的hstring来说,目前就不能通过[]访问元素
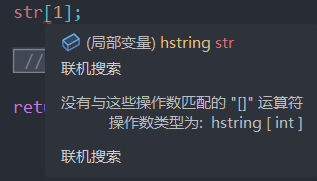
提示没有匹配的操作数。
1
2
3
| char &hstring::operator[](const unsigned short _index) const{
return this->c_str[_index];
}
|
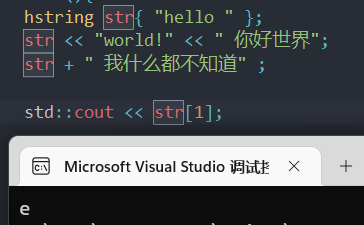
好似效果实现了。
另外,我们返回的是一个引用,当然指针也行,所以我们能够修改它
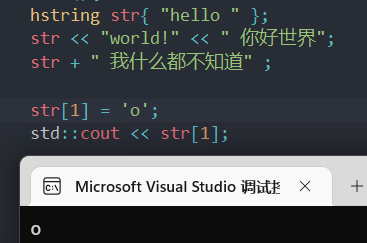
这也是数组那会的基本效果。
缺点是不能对中文有很好的支持,因为不能保证字符编码。
然后就是越界行为,目前是未定义的。
规范一下也不难,if判断一下。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| char &hstring::operator[](const unsigned short _index) const{
if (_index > hsLen){
return NULL;
}
else{
return this->c_str[_index];
}
}
|
但是返回空的话,NULL毕竟是0的意思,对于字符串引用类型不合适。
而且字符串结尾就是\0,有点相冲了。
就算用宏定义,因为是常量,又得修改函数返回类型,当函数返回类型也被修饰成const,那么之前的通过[]修改元素功能就失效了。
所以还是得在成员变量里加个。
在类的public下加了一个这个,至于用不用inline是看你项目属性要不要调到c++17标准,如果不是很有必要,就把初始化放外面就行了。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
char hstring::_NO_CHAR = -1;
char &hstring::operator[](const unsigned short _index) const{
if (_index > hsLen){
return _NO_CHAR;
}
else{
return this->c_str[_index];
}
}
|
这样又能保证能修改能访问,还能规范一下,虽然不是直接输出错误,但是应付if够用了。
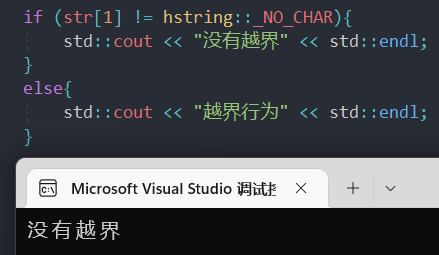
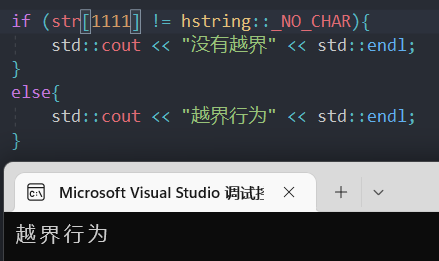
这样子修饰至少保证可阅读性
说要完善的话也还有可以加强的地方。看个人愿不愿意写了。
包括像数组一样申请。hstring strAry[100];
这里有个问题就是不存在默认的构造函数,
原因是我们那个默认构造函数的默认参数写在定义里了,改成写在声明就行了。
1
2
3
4
5
| hstring::hstring(char ch){
hsmLen = ch;
hsLen = 0;
c_str = new char[hsmLen];
}
|
这样就能用了。
修订
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| hstring &hstring::operator<<(const hstring &str){
unsigned short len = gethsLen(str.c_str);
len += hsLen - 1;
if (len > hsmLen){
char *rstr = c_str;
c_str = new char[len];
hsmLen = len;
memcpy(c_str,rstr,hsLen);
delete[] c_str;
}
memcpy(this->c_str + hsLen -1, str.c_str, len - hsLen + 1);
hsLen = len;
return *this;
}
|
没有刷新缓冲区的时候,字符串拷贝从c_str的长度-1开始是没问题的,
但当刷新了缓冲区,我们直接先清理掉c_str,就无法拷贝原有的内容了。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| #pragma once
#include<iostream>
class hstring{
private:
char *c_str;
unsigned short hsLen;
unsigned short hsmLen;
unsigned short gethsLen(const char *str) const;
void copyStrs(char *dest, const char *source);
public:
hstring(char ch=0x32);
hstring(const char *str);
hstring(const hstring &str);
hstring &operator=(const hstring &str);
hstring &operator<<(const hstring &str);
hstring &operator+(const hstring &str);
~hstring();
char *rtstr(){ return c_str; }
char &operator[](const unsigned short _index) const;
static char _NO_CHAR;
};
std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &_cout, hstring _str);
std::istream &operator>>(std::istream &_cin, hstring &_str);
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
|
#pragma once
#include "hstring.h"
#include<iostream>
#define no_char -1
char hstring::_NO_CHAR = -1;
hstring::hstring(char ch){
hsmLen = ch;
hsLen = 0;
c_str = new char[hsmLen];
}
hstring::hstring(const char *str):hstring(){
copyStrs(c_str, str);
}
hstring::hstring(const hstring &str):hstring(){
copyStrs(c_str, str.c_str);
}
hstring &hstring::operator=(const hstring &str){
copyStrs(c_str, str.c_str);
return *this;
}
hstring &hstring::operator<<(const hstring &str){
unsigned short len = gethsLen(str.c_str);
len += hsLen - 1;
if (len > hsmLen){
char *rstr = c_str;
c_str = new char[len];
hsmLen = len;
memcpy(c_str,rstr,hsLen);
delete[] c_str;
}
memcpy(this->c_str + hsLen -1, str.c_str, len - hsLen + 1);
hsLen = len;
return *this;
}
hstring &hstring::operator+(const hstring &str){
return *this << str;
}
hstring::~hstring(){
if (c_str != nullptr) delete[] c_str;
}
char &hstring::operator[](const unsigned short _index) const{
if (_index > hsLen){
return _NO_CHAR;
}
else{
return this->c_str[_index];
}
}
unsigned short hstring::gethsLen(const char *str) const{
unsigned short len = 0;
while (str[len++] != '\0');
return len;
}
void hstring::copyStrs(char *dest, const char *source){
unsigned short len = gethsLen(source);
if (len > hsmLen){
delete[] c_str;
c_str = new char[len];
hsmLen = len;
}
memcpy(c_str, source, len);
hsLen = len;
}
std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &_cout, hstring _str){
_cout << _str.rtstr();
return _cout;
}
std::istream &operator>>(std::istream &_cin, hstring &_str){
char _len[0xff];
_cin >> _len;
_str = _len;
return _cin;
}
|
结语
对hstring的补充~